
EmNet Project

 |
EmNet Project |

|
The main directions of activities
According to the decision of European Mathematical Council, a special unprofitable organization- European Mathematical Trust was created to give the project administrative and financial support.
Academic and business partners in Europe:
The Chairmen of the National committees together with the observers from East-European countries form Euromath Advisory Board under the rule of prof. Jose Luis Vicente, Spain.
The Euromat-Center attached to Copenhagen University was established in January, 1990, to support the project technically.
Today Euromat-Center is the main operating center of EmNet network in Europe. Simultaneously Euromat-Center is entrusted with user support.
Distribution of the EmNet program to the countries
of Central and Eastern Europe
In 1990-1994 several universities of Central and Eastern Europe received
financial support from EC within the TEMPUS program,
including computer equipment. Within the program significant assistance
was also granted to the basic mathematical centers of these
countries. It became the base for creation of the EmNet
services in these countries.
In 1993 200.000 ECU was allotted by European Commission within the COST program to supply the EmNet/C&E project, aimed at spread of the EmNet network infrastructure and service in the Central and Eastern Europe countries. The following countries take part in it: Albania, Bulgaria, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Slovakia, Czechia, Estonia.
In November, 1993, a constituent meeting of the EmNet/C&E program took place in Sofia (Bulgaria).
In 1993 the EmNet/NIS project , consisting of two phases, was supported by European Commission by means of INTAS association.
The project EmNet/fSU/phase-I (EmNet/NIS/Phase-I) proposes foundation of 8 regional centers of the EmNet network on the territories of Russia, Ukraine and Georgia. The total financing support of the project by EC is 240.000 ECU. The project will last 15 months.
In January 1994 a constituent meeting of the project participants took place in EIMI (Saint-Petersburg).
The participants of the project are:
 The full list of the project Phase l participants.
The full list of the project Phase l participants.
The Russian part of the project has extra financing from RBRF and RAS.
The project EmNet/fSU/phase-II (EmNet/NIS/Phase-II) is aimed at creation of 9 regional EuroMat centers located in Russia, Ukraine and Georgia. The total finance support from EC is 325.000 ECU. The duration of the project is 36 months.
A constituent meeting of the regional coordinators of the project and signing of the contract took place in April 1995. The regional zones on the USSR's territory were distributed as follows
The map of the participants of the project EmNet/NIS/Phase-II:
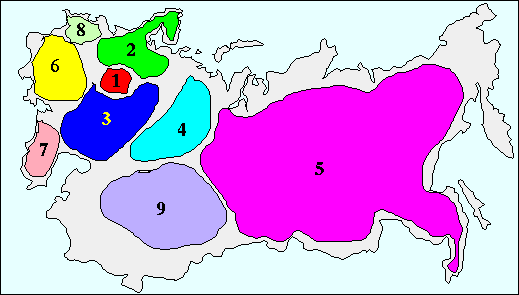
 The full list of the participants of the project Phase II.
The full list of the participants of the project Phase II.
Participation in creation of pan-European network of EmNet centers.
The situation in Western Europe:
Highly developed structure of academic scientific-research
computer networks in Western Europe allows to concentrate
mainly on the development of the
information resources and services of the EmNet
network. Therefore EmNet located on the territory of Western Europe
is a typical example of the logical object-oriented network.
The only exception is the situation when special wide-band channels are necessary for
particular applications (VBN, Germany).
An example of EmNet-center: EuromathCenter attached to Copenhagen University:approximately 10 employs, equipment - DECstations 5000 and 3100, SUNSPARCstations, IBM RS/6000, X-terminals.
The situation in Eastern Europe:
The situation in Eastern Europe varies.
On the one hand there are countries with relatively
developed infrastructure of computer networks (Hungary, Czechia),
on the other hand there are countries with absence of
computer networks (Albania). In the first case it is
possible to rely on public computer networks, in the
second, it is necessary to take part in creation of
national academic networks.
The situation in CIS:
Unfortunately there is no united academic
data transfer system on the territory of former
USSR today. Nowadays there are a number of
non-commercial academic networks that are known in
the West as "campus-wide" networks with some
elements of inter-city infrastructure. Practically
there are no commercial TCP/IP networks. The main
function of commercial networks is E-mail delivering but
this is done in a packet mode (UUCP) as a rule.
Therefore, for reaching required connectivity between the EmNet centers
it is necessary to allot some subsidy for organization of data transfer channels.
International connectivity is held by both non-commercial channels of public usage
(channels financed by MNF, RFFA) and within the EmNet project collaboration.
The Euromath system - a professionally oriented system of document preparation and exchange.
The Euromath system is a professional system of
preparation and exchange of mathematical documents,
developed on the base of structural editor-Grif, created by V.Quint (Grenoble)
and then being developed and supported by GRIF SA company
(St. Quentin).
Euromath system is based on the operating system UNIX
and graphics shell X-Windows. Nowdays the system
exists on the following
platforms: SUN4 - SUNOS, DECstations - ULTRIX, IBM
RS/6000 - AIX, HP - HP-UX. In the nearest
future an appearance of a version for
OS Solaris 2.*. is expected.
The minimum requirements to the platform are: 16 Mb RAM and 30 Mb free disk space.
Access to the data banks,
containing mathematical information.
Two data banks are used
most often within the EmNet program - the AMSMATH system, containing the on-line
version of the review magazine Mathematical Review, belonging to AMS
and the international bank in
FIZ, Karlsruhe, containing
information from the magazine "Zentralblatt fur Mathematik".
AMSMATH bank is supported by the ESA-IRS program (European Space Agency - Information Retrieval Service). The bank contains 3 bases - MATHHIST (1959 - 72) , MATHREVIEWS (1973 - 84), MATHSCI(1985-nv). The data bank FIZ works within the international scientific- technical network STN. The banks give the following bibliographic information about mathematical publications: